Use As Food
Makes good poi of a light gray color.
Distribution
Found mainly on Hawai‘i in small patches, mainly under dryland culture (māla).
General Characteristics
Short to medium in height, moderately spreading, stocky, maturing within 7 to 12 months, producing from 5 to 10 ‘ohā; readily identified by green- and white- patchy color (mottled) lū ‘au (leaves).
Ha (Petiole)
50 to 75 cm. long, fairly rigid, green— and white-striped. According to Jerry Konanui, the hā (petiole) is green with white stripes. Sometimes pink will show at the edge (lihi). The color of the kōhina (ring at the base) may change between generations. It may be a pale pink ring or a white ring. The hā is white for 3 to 4 cm. above the kōhina.
Lau or Lu'au(Leaf Blade)
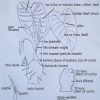
35 to 50 cm. long, 25 to 35 cm, wide, 30 to 40 cm. from tip to base of sinus (māwae), narrow arrow head-shaped (sagittate), fairly firm in texture, slightly concave (curve inward), green- and white— patchy color (mottled) ; margins wave-like (undulate); piko small, yellowish; round leaf section (lobes) acute with very narrow lihi māwae (sinus).
'I'o kalo (Corm)
Flesh light pink with pink fibers.
Pua (Flower)
H& #257; (peduncle) green- and white-patchy color (mottled); flower cover (spathe) 17.5 to 18 cm. long, the lower tubular portion about 2.5 cm. long, green—and white—patchy color (mottled), the upper portion yellow patchy color (mottled) with white, slightly open near constriction (skinny part of flower); spadix (spike of flower) 6 cm. long, the sterile appendage (tip of flower’s spike) 7 to 8 mm. long.
Remarks
This variety displays true variegation, and the striking green and white mottling of the leaves makes the plant very attractive. The amount of white area varies to a certain extent, according to environmental conditions. 91. ‘Elepaio Hā Uliuli and 23. ‘Elepaio Hā Kea are similar in appearance with their spotted leaves. The differences are, 1. The lū ‘au (leaf) of ‘Elepaio Hā Uliuli is more ovate (round) than the leaf of ‘Elepaio Hā Kea, which is more narrow (sagittate). 2. The Hā of ‘Elepaio Hā Uliuli is a darker red color at maturity. ‘Elepaio Hā Kea is green. 3. The corm color of ‘Elepaio Hā Uliuli is white, with yellowish fibers. The corm color of ‘Elepaio Hā Kea is light pink with pink fibers.